|
Chemguide: Support for CIE A level Chemistry Learning outcome 34: Nitrogen compounds 34.1: Primary and secondary amines Learning outcome 34.1.2 This statement is just a repeat of statement 33.3.2(e) in the acyl chloride section. Read the whole of the page about the reaction of acyl chlorides with ammonia or primary amines. In statement 33.3.2(e), CIE make clear that they just want you to produce the N-substituted amide and HCl. Ignore the follow-up reactions involving the reaction of the HCl formed with excess ammonia or amine. So with ammonia or a primary amine, you would use the initial equation for the reaction as in the examples given on the Chemguide page. In the phenylamine case, that equation would be:
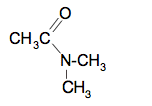
The syllabus also talks about secondary amines which aren't covered on that Chemguide page. The equation for the dimethylamine is:
The structure of the organic product is:
In every case, a hydrogen attached to the nitrogen and the chlorine in the COCl group come off as HCl, and what's left over joins together. You should have noticed the term "condensation reaction" in the syllabus. A condensation reaction is one in which two molecules combine to make a larger one with the loss of a small molecule between them during the reaction. The small molecule being lost here is HCl.
© Jim Clark 2020 |